
If you are an online merchant or work for one, I want to help you understand the importance of certain payment systems, various payment instruments, and its features for your commercial success. If you are a consumer, I hope it will make you more aware and – as a result – safer and more comfortable while shopping online.
So, let’s hit the road!
What are Payment Systems?
A Payment System is a mechanism that facilitates the transfer of value between a payer and a beneficiary by which the payer discharges the payment obligations to the beneficiary. Payments are essentially transportation tasks as funds are transferred from payer to payee following established payments flows that are characteristic of a given payment instrument. The payment system enables a two-way flow of payments in exchange for goods and services in the economy. Payment systems help consumers to transfer funds to each other.
Generally the payee has provided some kind of service or goods to the payer, who will in return pay an agreed amount of money against a request for payment, usually an invoice document, as part of the invoicing process.
Types of payment instrument & Mechanisms:
There are several types of payments available:
1) Credit Card:
A credit card is a small plastic card issued to users as a system of payment. It allows its holder to buy goods and services based on the holder’s promise to pay for these goods and services. A credit card allows the consumers a continuing balance of debt, subject to interest being charged. Most credit cards are issued by banks.
Credit Cards History
It was first used in the 1920s, in the United States, specifically to sell fuel to a growing number of automobile owners. Western Union had begun issuing charge cards to its frequent customers in 1921. Some charge cards were printed on paper card stock, but were easily counterfeited.
In September 1958, Bank of America launched the BankAmericard. It became the first successful recognizably modern credit card, and with its overseas affiliates, eventually evolved into the Visa system in 1976

A credit card system is a credit facility extended to a user who is issued a plastic card that can be used in place of cash for making any type of payment/purchase. Credit Card enables its holder to buy goods and services with a credit line given by credit card issuer. The institution which issues the card has a tie-up with the concerned merchant establishment and the card-issuing organization, if different, to facilitate this arrangement. The amounts charged to the customer are paid by the card issuer to the merchant and subsequently billed to the customer. Funds are settled at a later date. Cardholders are billed on a monthly basis and bear financial charges (interest) on outstanding amounts if payments are not made by the due date. Therefore, rather than paying the seller directly, the buyer pays off its bill to the credit card company. If the entire balance of the bill is not paid, the company is authorized to charge interest on the buyer’s remaining balance. Credit cards can be used for both online purchases and at physical retailers. Credit cards are issued through commercial banks and/or other issuers. A credit cardholder may not be an account holder in the bank which issues the credit card.
Let’s take a look at the front side of the card, which is the fanciest shiny face of the card.
- Issuing bank name or logo – The logo of the bank that has provided you the debit/credit card. Few banks just print their name instead of adding their logo. This can be found in the top right or left corner of the card
- Card product type – Every card will have their product name, e.g. Platinum, Titanium, Jet Privilege, etc. Every card product has features and offerings defined by their banks. You should definitely read the most important terms and conditions (MITC) at least once in your lifetime to understand annual fees, late payment charges, etc that vary per card
- EMV chip – Newly generated credit and debit cards in India have a metal square chip on the front side of the card, which stores sensitive data and provides better security as compared to the traditional magnetic strip that is found on the backside of the card. EMV chips are also used by the POS machine and the ATM machine to perform transactions. EMV chips are difficult to clone and hence, fraud related to cloning of comparatively a magnetic strip card is relatively low
- Contactless icon – You might notice a wifi or wave type of symbol on top of your card – that’s the icon of the contactless feature of a card. You can pay on a POS machine without even entering the PIN. This works only when the amount is less than Rs. 2000 and the machine also has this wifi or wave symbol. If the total amount is above Rs. 2000 then you would be asked to enter the PIN. The purpose of this feature is so you don’t have to hand over cards to anyone and it would work by just tapping on the machine. Contactless payments offer the same level of security as a chip card
- Card network logo – Often called ‘card brands’ or ‘card schemes,’ these are companies that connect the issuing bank and acquiring bank to facilitate online payment. Rupay, Visa, MasterCard or Amex are examples of this.
- Card number: These 14 to 19-digit card numbers are the most sensitive element of your card. Card numbers vary in length as per the issuing bank. You would be surprised to know that these are not just unique 16-digit numbers but there is a logic to generate the Card Number.
- First 6 digits: Bank Identification Number(BIN) – every bank in the world will be issued with a 6-digit number by card networks (Visa/MasterCard), which is used to identify the issuer of the card. By just looking at the first 6 digits of your card, one can know the card network and issuing bank of your card.
- Digits 7 – 15: Primary Account Number (PAN), which is uniquely assigned by the bank to every cardholder to identify them. This is very critical information and that’s why you must have seen that these are masked in most bank account statements.
- Digit 16 – Often called a check digit that is determined mathematically by a formula called the Luhn Algorithm. This digit is derived by applying the Luhn Algorithm on the previous 15 digits of the card. That’s why you might have noticed whenever you enter a wrong card number during online checkout, it will immediately highlight that the card number is incorrect as the system performs a check based on the Luhn Algorithm.
Fun Fact: Did you know that the very first digit of your card represents the card network? Number 3 is for Amex, 4 is for Visa, 5 is for Mastercard, 6 is for Rupay. Go ahead and verify this against your cards!
7. Validity dates: A few cards have both the issuing date and expiry date, but some cards will have just the expiry date. This is mostly used to shop online and also to know the validity of your card. In case your card is about to expire, the bank will automatically send you the new card to your mailing address before your card expiry date. That’s why it’s always said to have your postal address updated with your bank.
8. Cardholder name – Your name is embossed on the card to provide you the feel of having a personalized prized possession. If your card was issued as part of your instant account opening process, then your name won’t be available. You can always reach out to your bank to reissue the card with your name on it.
How they work
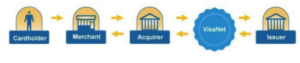
- A cardholder selects his or her goods and presents his or her card for payment.
- The merchant submits the purchase details to its financial institution for approval.
- The merchant’s financial institution sends the purchase details to the cardholder’s financial institution.
- The merchant receives a “payment guarantee,” and the cardholder receives the goods.
- The cardholder’s financial institution remits to the merchant’s financial institution the retail price less the interchange rate.
- The merchant’s financial institution remits to the merchant the retail price less the Merchant Discount or Merchant Service fee, which may include interchange, the cost of transaction processing, terminal rental and customer service, and the merchant financial institution’s or processor’s margin, among other costs.
- This charge is negotiated directly between the merchant’s financial institution and the merchant.
Electronic verification systems allow merchants to verify in a few seconds at the time of purchase that the card is valid and the credit card customer has sufficient credit to cover the purchase.
The verification is performed using a point of sale (POS) system with a communications link to the merchant’s acquiring bank. Data from the card is obtained from a magnetic stripe or chip on the card.
Credit Cards Payment
A credit card statement is sent monthly indicating the purchases made on the card, any outstanding fees, and the total amount owed.
The cardholder must pay a defined minimum proportion of the bill by a due date or a higher amount up to the entire amount owed. The bank charges interest on the amount owed if the balance is not paid in full. If the cardholder fails to make at least the minimum payment by the due date, the bank may impose a ”late fee” and/or other penalties. Some banks arrange for automatic payments to be deducted from the user’s bank account to avoid such penalties.
Top Credit cards in India
| Card Name | Category | Annual Fee | Joining Fee | Late Payment Fee |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICICI Bank Emerald Credit Card | Lifestyle | ₹ 12,000 | ₹ 12,000 | Nil |
| Jet Privilege HDFC Bank World Card | Travel and Airline | ₹ 2,500 | Nil | ₹ 750 |
| Infinia Card | Lifestyle | ₹ 10,000 | ₹ 10,000 | ₹ 750 |
| Diners Club Black Card | Lifestyle | ₹ 10,000 | Nil | ₹ 750 |
| Jet Privilege Diners Card | Lifestyle | ₹ 10,000 | Nil | ₹ 750 |
| Premier Master Card | Premium | Nil | Nil | ₹ 750 |
| Instant Platinum Card | Low Fee | Nil | Nil | ₹ 750 |
| Insta Easy Card | Low Fee | Nil | Nil | ₹ 700 |
| Doctors Superia Card | Premium | ₹ 1,000 | Nil | ₹ 750 |
| Signature Cards with Lifestyle benefits | Lifestyle | Nil | ₹ 5,000 | ₹ 700 |
What Types of Credit Cards Are Available?
Most major credit cards—which include Visa, Mastercard, Discover, and American Express—are issued by banks, credit unions, or other financial institutions.
In addition to the standard bank-issued credit card, here are a few other common card types:
-
- Balance Transfer Card: The credit cards with balance transfer allow you to transfer the outstanding balance of any credit card to another card.
- Rewards Card: The rewards cards are designed to suit shoppers. When you use a rewards card to make a purchase, you earn certain reward points. For example, some cards will give 4 reward points for each Rs. 100 spent, or 6 reward points for each Rs. 100 spent. The rewards vary from bank to bank.
- Business Credit Card: These cards are designed for companies, corporates, big and small businesses and partnerships. The card is mainly held by the employer but can also be issued to employees in which employer can cap the credit limit.
- Cashback Card: Everybody like to earn some money while spending some, that’s why cashback is so popular. The amount of cashback will vary for each issuer.
- Co-branded Cards: Many issuers collaborate with brands to come up with credit cards that has special discount and deals for that brand. Some examples of co-branded credit cards are; Yatra SBI card, HDFC Snapdeal credit card.
- Credit cards for Women: Some credit cards are specifically designed for women. It provides cashback, rewards and exciting deals for women on various kinds of transactions such as shopping, dinning, surcharge waiver, etc.
- Secured Credit Cards: A credit card against which you are required to submit a certain amount as deposit is called the secured credit card. Under this, you are required to submit the amount equal to or slightly more than the allotted credit limit. This card is best for those who are new to credit or wants to improve his credit history.
- Prepaid Credit Card: As the name suggests, this card is prefilled with some amount. Usually this type of credit card is used as forex credit card. These cards are as good as debit card since the amount you spend will from the money you deposited earlier.
- Premium Credit Cards: As the name suggests its a credit card for premium customers. It offers premium services and offers such as club memberships, dinning privileges, etc. Such cards has high minimum spending limits and high income as an eligibility criteria.
- Student Credit Card: These credit cards are specifically designed for college students. The student should be above 18 years, and need to submit employment document and income tax return.
What Fees Do Credit Cards Charge?
Interest aside, credit cards do have other fees to be aware of, including:
- Late fees: The issuer charges these when you don’t make your minimum payment by the statement due date.
- Annual fees: On certain cards, the issuer charges this once a year to cover the benefits provided by the card. For your first credit card, however, we recommend looking for one without an annual fee. (That’s because you should keep it open for as long as possible — without worrying whether you’re getting enough value from the annual fee.)
- Cash advance fees: If you choose to take out cash with your credit card, you’ll pay hefty fees. We strongly advise against using a credit card for cash advances — if you don’t have the money, don’t use your card.
- Balance transfer fees: If you transfer a balance from another credit card, which can be a smart strategy with 0% APR(annual percentage rate) cards, you’ll often pay a fee equal to a percentage of the balance transferred.
- Foreign transaction fees: When you make purchases in another currency, the issuer may charge a fee — so if you travel abroad frequently, you should look for a card without foreign transaction fees.
Credit Cards Interest
The general calculation formula most financial institutions use to determine the amount of interest to be charged is:
- APR/100 x ADB/365 x number of days revolved.
- APR: Annual Percentage Rate
- ADB: Average Daily Balance
Credit Cards Benefits to Customers
The main benefit is convenience as it eliminates the need to carry any cash for most purposes. It is also considered a quick loan that can be financed for a short term.
Many credit cards offer rewards and benefits packages; enhanced product warranties at no cost, free loss/damage coverage on new purchases, and points which may be redeemed for cash, products, or airline tickets.
Credit Cards Benefits to Merchants
For merchants, a credit card transaction is often more secure than other forms of payment, such as checks, because the issuing bank commits to pay the merchant the moment the transaction is authorized, regardless of whether the consumer defaults on the credit card payment. In most cases, cards are even more secure than cash, because they discourage theft by the merchant’s employees and reduce the amount of cash on the premises.
Credit Cards Cost to Merchants
Merchants are charged several fees for the privilege of accepting credit cards. The merchant is usually charged a commission of around 1 to 3 per-cent of the value of each transaction paid for by credit card. The merchant may also pay a variable charge, called an interchange rate, for each transaction.
Merchants with very low average transaction prices or very high average transaction prices are more averse to accepting credit cards.
Credit Cards Cost to Banks
Credit card issuers (banks) have several types of costs:
- Interest expenses: Banks generally borrow the money they then lend to their customers. If the card issuer charges 15% on money lent to users, and it costs 5% to borrow the money to lend, and the balance sits with the cardholder for a year, the issuer earns 10% on the loan. This 10% difference is the “net interest spread” and the 5% is the “interest expense”.
- Operating costs: This is the cost of running the credit card portfolio including everything from paying the executives who run the company to printing the plastics, to mailing the statements, to running the computers that keep track of every cardholder’s balance, to taking the many phone calls which cardholders place to their issuer, to protecting the customers from fraud rings. Marketing and promotional programs are also a significant portion of expenses.
- Charge offs: When a consumer becomes severely delinquent on a debt, the creditor may declare the debt to be a charge-off. A charge-off is considered to be “written off as uncollectable.” To banks, bad debts and even fraud are simply part of the cost of doing business.
- Rewards: Many credit card customers receive rewards, such as frequent flyer points, gift certificates, or cash back as an incentive to use the card. Depending on the type of card, rewards will generally cost the issuer between 0.25% and 2.0% of the spread.
- Fraud: When a card is stolen, or an unauthorized duplicate made, most card issuers will refund some or all of the charges that the customer has received for things they did not buy. Credit card fraud continues to be a major problem.
Credit Cards Revenue to Banks
The major income generators are:
- Interchange Fee (fees are typically from 1 to 6% of each sale)
- Interest on outstanding balance
- Other fees charged to the customer:
- Late payments or overdue payments
- Exceeding the credit limit on the card called over-limit fees
- Cash advances (often 3% of the amount)
- Transactions in a foreign currency (as much as 3% of the amount).
- Membership fees (annual or monthly)
- Exchange rate loading fees (sometimes these might not be reported on the customer’s statement, even when applied).
Important Credit Card Details
A credit card is one of the most important financial inventions in modern times that enables one to make online transactions easier. It allows a cardholder to purchase goods and services on credit and pay it back on a later set date. Besides, credit card benefits are such that using it over other modes of payments is a far better option and of course, it eliminates the need for you to carry cash everywhere. Some key credit card benefits are listed below.
- To build your credit score: Disciplined swiping of a credit card can help improve your credit score. The reason being, instant credit card issuer companies will report your payment activity to the credit bureaus. Moreover, a crucial credit card details is that no interest on your purchase is charged if you make the complete payment within the grace period. Hence, complete and timely repayment of your monthly bills will help improve and build your credit score faster.
- To avail instant loan: An important credit card information is that you can avail loan against your card if you have a good credit score. You also have the option to convert your purchases in Credit Card EMIs which can be paid during a pre-agreed loan tenure. The advantage of pre-approved credit card loans is that they have the fastest time when compared to other loans. You do not need any additional documents, while in case of a personal loan, some level of documentation is required. The interest rates of loans against these cards usually start from 11.50% per annum onwards and their tenure can go up to five years.
- To earn cashback and reward points: Another credit card benefit that you can take advantage of is the attractive reward points and cashback. These cashback and discounts reduce the cost of purchases. On the other hand, reward points can be redeemed for goods or services from partner stores. Hence, doing more online transactions using these cards will help you earn more such benefits.
- To save money on grocery shopping: For many people, grocery shopping is a regular task and therefore, no other option comes into our mind other than using these cards. Most of the cards have been affiliated with supermarkets, which means you can earn some additional cashback or discounts on your everyday shopping. The more you spend, the more you get a discount through these cards.
- To cut the cost of existing debts: The main advantage of using them is that it helps you get out of the vicious cycle of debt that only grows worse over time because of compounding interest rates. If you owe money on an existing credit card, you have the option to reduce the cost by transferring the outstanding balance to another such card which has a lower interest rate.
- To plan an international trip: If you are planning an overseas trip, using the best travel credit card will yield multiple benefits. Nowadays, international credit cards offer a low or no foreign currency transaction fee. Also, some cards offer international customer assistance which is helpful during your much-awaited trip. Plus, a lot of travel-oriented cards offer special discounts on flight tickets, car rentals, hotel bookings, etc.
- To earn free travels and hotel stays: Credit card apply online that offers rewards and perks on hotel stays. You can redeem the points for a free flight or a free hotel stay. You can make the best use of complimentary amenities for an exotic vacation or weekend getaway.
- Helps to save time: A credit card eliminates the need for you to carry cash everywhere. It also avoids the trouble of searching for ATMs and in turn, saves your time of visiting them.
- To track your expenses: Credit cards help you to keep track of your day-to-day expenses. Your statements include the name of the merchant, date of the transaction, and amount spent. Some cards also provide the year-end summary that helps while paying taxes.
Credit card benefits:
Credit card is simple and easy to use. Here are some of its benefits:
- Recurring Payments: You can use a credit card to set for recurring payments of your electricity bills, phone bills, etc.
- Free Credit: Each credit card has a grace period of 40-50 days. So, if you make a purchase and repay it completely within the grace period, then no interest will be levied. However, if for once the interest rate is charged on your bill, then the grace period will no longer be applicable.
- Credit Score: Not many people know, but the credit card is one of the best ways to improve your credit score or build a credit history for yourself.
- Convenience: Carrying cash everywhere no more feasible nowadays, nor it’s completely safe. However, you can easily carry a small plastic card with you wherever you go and make the transaction with a simple card swipe.
- Cashback and Discount: Credit card offers provide a host of benefits, cash back, and discount deals on store shopping, fuel, online shopping, dining, travel, etc.
- Rewards: Each time you use a credit card, you accumulate certain reward points based on the card and the bank. You have the option to redeem these points to get gifts and vouchers.
Submission, Clearing, and Settlement of Credit Card Transactions
By accepting credit cards at your store, you become an integral part of the payment processing system, which is why it is important that you develop a clear picture of the card transaction process: what it is, how it works, and who participates in it. This basic knowledge will help you understand the major payment processing components and how they affect the way you do business.
Now let’s understand the final three stages of the transaction process i.e — submission, clearing and settlement
The Card Transaction Process
The diagram below represents the stages of the credit card transaction process:
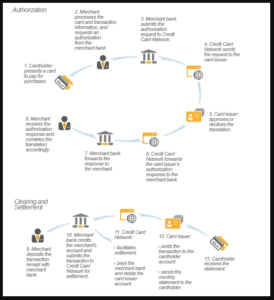
Let’s have a detailed look at the way MasterCard processes its transactions:
The Authorization Process
- The customer purchases goods or services from the merchant and swipes their credit or debit card through a point-of-sale (POS) terminal or device which captures the customer’s card information.
- The customer’s card information is transmitted to the merchant’s payment processor, who in turn passes the card information and transaction amount to the merchant’s bank (the acquirer, or acquiring bank). Note that some payment processors are also acquiring banks.
- The acquiring bank captures the transaction and forwards the information to the customer’s credit card network (e.g. Visa, Mastercard).
- The card association system then routes the transaction (the issuer, or issuing bank), and requests an approval. The transaction is approved or declined depending on the availability of funds and the status of the cardholder’s account. This approval process is known as authorization.
- The issuing bank sends the response back to the credit card network. If the authorization was approved, the issuing bank assigns and transmits an authorization code along with its response, and a hold is placed on the cardholder’s funds.
- The authorization code is sent from the card association to the acquiring bank.
- The credit card network sends the approval to the merchant’s payment processor, who in turn sends the approval to the acquiring bank.
- The acquiring bank routes the approval code or response to the merchant’s terminal. Depending on the merchant or transaction type, the merchant’s terminal may print a receipt for the customer to sign.
The Settlement Process
- At the end of each day, the merchant closes out the day’s sales and transmits the information to their payment processor, who in turn transmits the information to the acquiring bank. This step, in which the merchant initiates the transfer of funds to their account, is known as capture.
- The acquiring bank routes all transaction information to the credit card network for settlement, who in turn passes on all approved transactions to the cardholder’s issuing bank.
- The issuing bank transfers the funds to the merchant’s acquiring bank, minus the interchange fee.
- The acquiring bank then deposits the amount, less the discount fee, to the merchant’s bank account.
- The issuing bank bills the cardholder for the transaction.
2) Debit Card:
Debit Card is a payment card where the transaction amount is deducted directly from the card holder’s bank account upon authorization. Debit cards can be of two types, one which is linked to an account and is issued by banks to account holders only. Second could be pre-loaded cards where a certain amount is stored in the card. Generally, debit cards are also ATM cards. The mode of using debit cards and credit cards is generally the same. Hence Paying with a debit card takes the money directly out of the buyer’s account. It is almost like writing a personal cheque, but without the hassle of filling it out.
In addition, debit cards, also called “check cards,” offer the convenience of credit cards and many of the same consumer protections when issued by major payment processors such as Visa or Mastercard.

Components of a debit card
A debit card has the following details:
- The card number: this is a 16- digit number. The card number is unique and is not the same as the bank account number.
- The issue and expiration date: The issue date is also printed in the MM/YY format. The expiry date is also printed in the same MM/YY format.
- The Logo: The card has the logo of the bank that has issued it. It also has the logo which determines the type of debit card it is: Visa, Mastercard or RuPay logo.
- Customer service number: The toll-free number is printed on the back of the card. You can call this number in case of any questions or to report the loss or theft of your card.
- The signature bar: A signature bar is provided on the back of the card. It is important that you sign the bar as soon as you receive the card. This can help you to prevent fraudulent transactions. Some merchant retail outlets do not swipe the card unless the signature is verified.
- CVV number: Also known as the card verification value number, the CCV number is unique to every debit. This number needs to be provided at the time of making online payments. It provides an additional layer of security to the card.
Key takeaways:
- Debit cards eliminate the need to carry cash or physical checks to make purchases, and they can also be used at ATMs to withdraw cash.
- Debit cards usually have daily purchase limits, meaning it may not be possible to make an especially large purchase with a debit card.
- Debit card purchases can usually be made with or without a personal identification number (PIN).
- Some debit cards offer reward programs, similar to credit card reward programs, such as 1% back on all purchases.
Most people are used to using a debit card these days and many even use it on a daily basis, but there are pros and cons. Debit cards do have their critics though and not all financial experts think that over-reliance on a debit card over other methods of payment is always a good idea.
Debit cards can function in two ways:
- Like an ATM card for immediate withdrawals of cash
- Like a check when buying an item. The money used to pay for the transaction is usually deducted from your account within a day or two depending on when the retailer presents the transaction for payment.
Even though debit cards have become widely used, many people are unfamiliar with their advantages and disadvantages. Debit cards look like credit cards, but function like cash or personal checks.
Indeed like many things debit cards have their advantages and their disadvantages. Here are some of the most important explained:
Debit Card Use Advantages
There is certainly quite a lot to be said for the convenience of using a debit card as well as some distinct benefits:
- Safer than Cash – Carrying around large amounts of cash is never a good idea, but then again heading for a night out or to go shopping with just £20 in your wallet is simply not going to cut it most of time. As ATM machines can be found almost anywhere these days then a debit card allows you to only get out cash if you really need to while you use it to pay for many other purchases instead.
- Online Shopping and Bill Pay – Because a debit card can be used in the same way as a credit card it means that cardholders can take advantage of all the great online shopping opportunities that are out there as well as make regular bill payments online in many cases – saving you the hassle of paper checks, stamps and trips to the Post Office.
- Easier to Keep Track of Spending – Many people have done this at least once – written a paper check and then forgot to record the transaction in their check register. The end result is often very expensive (and often embarrassing) in terms of bounced check fees and overdraft charges. Debit card transactions are posted right away online – even credit transactions that do not “clear” immediately – so it is much easier to keep a daily eye on what you are spending and how much money you have left!
- Great for Those Without a Credit Card – If you have poor credit – or no credit at all – getting a credit card can be hard and that can potentially prevent you from doing all kinds of things like renting a car or booking travel arrangements. Since a debit card can be used in lieu of a credit card in most situations these days they can really help people who are still trying to build their credit out.
- Teaching Tools – Those under the age of eighteen cannot apply for a credit card of any kind and even when they do reach their 18th birthday the rules governing credit cards are much tighter than they once were and getting a student credit card is much harder than it once was. There are a growing number of prepaid credit cards that are specifically designed for teens though and using one can be a great way to learn all important money management skills – as well as being “cooler” than having to pay in cash.
- Less Loss Potential – If a £20 note falls out of your pocket chances are it is gone forever. If you lose a debit card however once you report the loss to the bank within 48 hours the most the law says you can be held responsible for is £50 and in fact many debit cards are covered by either VISA or Mastercard’s zero liability policy.
Debit Card Disadvantages
The downsides associated with debit card use mainly revolve around the fees charged but there are one or two other disadvantages as well:
- More Fees: There are potentially quite a few fees involved in regular debit card use that can add up quite quickly. The largest of these fees tends to be the charges you incur when you use an ATM to withdraw cash – if you use an ATM that does not belong to your card issuer’s network then you may be charged two fees – one by your own bank and one by the ATM owner and these days these fees when combined can be as high as £2 per withdrawal. Monthly fees and PIN transaction fees can add up as well. Many of these fees can be avoided though if you shop around carefully as some debit cards offer a much better value in terms of fees than others.
- Dealing with Problem Transactions – Sometimes people are faced with a dilemma when making larger purchases or purchases online – which should they use, their credit card or their debit card? In one respect paying with a debit card may be a better idea as the item is paid in full. On the other hand though if there is a problem with a transaction or you need to return an item getting your money back on a debit card can be a lengthy and confusing process, whereas if you had opted to use a credit card the transaction would simply be reversed and you would not be “out” the money.
- Recurring Transactions – As people spend more and more time on the Internet they tend to sign up for all kinds of services that have a monthly charge attached to them – everything from a TV service like Netflix to music services like Spotify and 101 things in between.
Most of these services accept a debit card as readily as they accept a debit card. The danger is though that you will forget that one of these payments is due and the charge will be made when you do not quite have enough money in your bank account to cover it and you will be tied up with overdraft fees and cancelled subscriptions, something that would probably not be an issue with a credit card.
In the end how and when they use a debit card is up to the individual. With some careful shopping around you can find debit cards that have lower fees attached to them and there are ways you can minimize the fees you are charged – asking for cash back when making a debit card purchase instead of withdrawing money from an ATM for example. Life without a debit card can be rough these days so using them occasionally is almost a must, and can be quite beneficial if you use it sensibly.
Some Guidelines
- Guard your debit card against loss or theft. Keep it in a safe place just like cash, credit cards or checks.
- If you lose your debit card, notify your financial institution immediately.
- Choose a PIN number that only you know. It is recommended, you don’t use your phone number or birthday.
- Guard your PIN number. Memorize it and never write it on anything you keep with you.
- Keep receipts from all your debit card transactions for your records.
- Review your statements immediately and investigate any unknown transactions.
- Use chip-enabled technology if available. For the most secure transaction, if a retailer offers a chip-enabled terminal, use it instead of swiping the magnetic strip.
What Is The Difference Between Credit Card And Debit Card?
While both the cards look similar in appearance, they function differently. A debit card is linked to the bank account of the customer and hence, once swiped, the amount is directly deducted from the bank account. Credit card, on the other hand, allows the cardholder to purchase goods and services on credit and pay it back over time. This card is issued by the banks on the basis of the credit history and eligibility of the customers.
| Credit Card | Debit Card |
|---|---|
| Credit cards allow the cardholders to purchase goods and services on credit and pay it back over time | In case of a debit card, the amount is instantly deducted from your bank account |
| You have the option to convert your credit card purchases into EMIs | No credit facility is available, as you pay instantly from your own funds |
| Provides better security in case of faulty transactions | Provides less security in case of faulty transactions |
| Typically offered with joining and annual fees | Typically issued free with your savings account |
| The penalty is charged on non-payment or late payment of your credit card dues | Penalty charges are not applicable in case of debit cards |
Why Is Credit Card A Better Option Than A Debit Card?
- Gives short term interest free credit: When you swipe your debit card, payment is instantly deducted from your bank account. However, in case of a credit card, the payment is done by the bank to the vendor and no amount is charged from the card holder. The card holder can repay the amount within the grace period which can go up to 45-50 days without requiring to pay interest during this period.
- Helps to improve CIBIL score: A good credit score has become the basis for loan eligibility and approvals by all the other financial institutions and banks. Timely payment of all your credit card dues goes a long way in improving or building your credit score. But make sure to pay your credit card dues on time, otherwise, it can reduce your credit score. Regular and disciplined usage of credit card is typically is the first step towards building a credit history for a first-time borrower
- Rewards and cashback: Credit cards offer various kinds of rewards to the customers such as air miles, fuel points, free gifts, cashback rewards, etc. In the case of debit cards, such rewards are a rarity as most debit cards are not part of reward programs.
- EMI Facility: If you buy a product using a debit card, you are liable to pay the entire amount in one go. On the other hand, if you are using a credit card, you have an option to convert your purchases into EMIs (Equated monthly installments) of up to 24 months. However, you have to pay an interest of approximately 1% to 2% every month on the outstanding amount along with additional charges such as service tax
- Protection from fraud: Credit cards provide better security in case of lost/stolen cards or fraudulent transactions. Most of the credit cards have liability protection feature which protects the cardholder from any unauthorized transaction. Moreover, you also benefit from the chargeback option and protection plans. These features are not available on a debit card. If a fraudulent activity takes place, the amount is instantly deducted from the debit card.
- Purchase protection: Credit card gives you the opportunity to withhold payment in case you find any defect or problem with the product purchased. By contacting the credit card company and disputing the charge, you can prompt an investigation that could potentially result in a refund. In the case of a debit card, there is zero liability protection for the cardholders.
Conclusion: Disciplined swiping of a credit card can provide huge financial benefits to the cardholder. However, if you risk using the card without disciplined repayment, then better stick to debit cards.
| Spending With Debit and Credit Cards | |
|---|---|
| Use Debit Cards To… | Use Credit Cards To… |
| Stay out of debt
Avoid annual fees Avoid credit scrutiny Simplify finances Make ATM withdrawals |
Complete everyday purchases without a PIN
Build credit Pay after a grace period Spend at higher limits Receive robust fraud protection Qualify for rewards |
3) Netbanking:
Internet banking, also known as online banking or e-banking or Net Banking is a facility offered by banks and financial institutions that allow customers to use banking services over the internet. Customers need not visit their bank’s branch office to avail each and every small service. Not all account holders get access to internet banking. If you would like to use internet banking services, you must register for the facility while opening the account or later. You have to use the registered customer ID and password to log into your internet banking account.

Features of Online Banking
- Check the account statement online.
- Open a fixed deposit account.
- Pay utility bills such as water bill and electricity bill.
- Make merchant payments.
- Transfer funds.
- Order for a cheque book.
- Buy general insurance.
- Recharge prepaid mobile/DTH.
Advantages of Internet Banking
The advantages of internet banking are as follows:
- Availability: You can avail the banking services round the clock throughout the year. Most of the services offered are not time-restricted; you can check your account balance at any time and transfer funds without having to wait for the bank to open.
- Easy to Operate: Using the services offered by online banking is simple and easy. Many find transacting online a lot easier than visiting the branch for the same.
- Convenience: You need not leave your chores behind and go stand in a queue at the bank branch. You can complete your transactions from wherever you are. Pay utility bills, recurring deposit account instalments, and others using online banking.
- Time Efficient: You can complete any transaction in a matter of a few minutes via internet banking. Funds can be transferred to any account within the country or open a fixed deposit account within no time on Netbanking.
- Activity Tracking: When you make a transaction at the bank branch, you will receive an acknowledgement receipt. There are possibilities of you losing it. In contrast, all the transactions you perform on a bank’s internet banking portal will be recorded. You can show this as proof of the transaction if need be. Details such as the payee’s name, bank account number, the amount paid, the date and time of payment, and remarks if any will be recorded as well.
Disadvantages of Internet/Online Banking
The disadvantages of internet banking are as follows:
- Internet Requirement: An uninterrupted internet connection is a foremost requirement to use internet banking services. If you do not have access to the internet, you cannot make use of any facilities offered online. Similarly, if the bank servers are down due to any technical issues on their part, you cannot access net banking services.
- Transaction Security: No matter how much precautions banks take to provide a secure network, online banking transactions are still susceptible to hackers. Irrespective of the advanced encryption methods used to keep user data safe, there have been cases where the transaction data is compromised. This may cause a major threat such as using the data illegally for the hacker’s benefit.
- Difficult for Beginners: There are people in India who have been living lives far away from the web of the internet. It might seem a whole new deal for them to understand how internet banking works. Worse still, if there is nobody who can explain them on how internet banking works and the process flow of how to go about it. It will be very difficult for inexperienced beginners to figure it out for themselves.
- Securing Password: Every internet banking account requires the password to be entered in order to access the services. Therefore, the password plays a key role in maintaining integrity. If the password is revealed to others, they may utilize the information to devise some fraud. Also, the chosen password must comply with the rules stated by the banks. Individuals must change the password frequently to avoid password theft which can be a hassle to remember by the account holder himself.
4) Mobile Wallet
Mobile Wallet is a type of payment service through which individuals can receive and send money by mobile devices. It is a form of an e-commerce model designed for the mobile devices for the convenience and ease of access. Mobile Wallet is also known as Mobile Money or Mobile Money Transfer.

Mobile Wallet is also known as mWallet, digital wallet, or eWallet. It is basically referred to a mobile technology that is used the same as a real wallet.
It is the digital version of the wallet that you can carry in your pocket. It stores payment details like credit or debit card and cash balances which can be used to make payments.
In other words, it is a digital technology to pay your bills online instantly without having to pay by cash or use your credit or debit card all the time. It acts like a virtual wallet, which can be preloaded with your preferred amount of money from your bank account or credit or debit cards and used to spend it online. You can simply use your smartphone or a tablet to make the payment. With e-Wallet apps installed on your mobile, you need not to carry cash in your hands every time.
Things you can do with your mobile wallets
- Transfer money to others
- Recharge your DTH, mobile and data packs
- Track your monthly expenditure
- Save money by saving the cost of ‘middlemen’
- Make utility and bill payments
- Book Airline, bus and train tickets
Types of mobile wallets
Mobile wallets are categorized into three main segments: closed, semi-closed and open.
- Closed wallets: are linked to a merchant or private company where you can use the money only for direct purchase from the specific merchant. Money from these wallets cannot be transferred to your bank account. Examples of these wallets are Amazon Pay and Ola Money, to name a few.
- Semi-closed wallets can be used with multiple merchants as long as they have a contract with the payment portal. Though you can receive money in semi-closed wallets into your bank account, you cannot withdraw it as cash. Examples of wallets like these are PayTM, Freecharge, and Mobikwik.
- Open wallets: on the other hand, are not limited to the other two. This type of wallet is issued either directly by a bank or by them to a third party. Money in this wallet can be used for any transaction and users can withdraw money remitted to their account in cash. Examples of these mobile money wallets are PayPal, and Vodafone M-Pesa.
How Does a Digital Wallet Work?
- A digital wallet saves the card details of the user and lets him/her make purchases online. For example, a MasterPass digital wallet asks customers to first register for the service by entering card details.
- The information then has to be verified through an OPT authentication process, post which registration will be complete.
- After this process is complete, one can choose the ‘Buy with MasterPass’ option as a payment mode on e-commerce websites that have this option.
- The payment can be made by entering the MasterPass card ID and password and the transaction will be authenticated through a 3D-secure PIN or OTP
How do you transfer money to a mobile wallet?

So how does a mobile wallet work? To send money to a mobile wallet, first, make sure that the receiver has one set up on their phone. It’s a straightforward process- simply download an app and install it. You then need to pop into an agent, provide the receiver’s mobile number and hand over the amount you want to send. The money appears in the receiver’s wallet instantly.
Customers can access all of the stored information simply by opening an app on their phones by entering a PIN, password or fingerprint, and then selecting the information that they need to access. This app then utilizes information transfer technology like Near-Field Communications (NFC) to interact with ready-to-pay terminals in the mobile wallet.
- Mobile Wallet securely stores your credit or debit card.
- They can also store your loyalty cards, coupons, tickets, etc.
- They communicate with the terminals using various techniques or technologies.
Therefore, without a device that receives mobile wallet information, you will not be able to take advantage of this increasingly popular payment mechanism.
It can also be understood that in mobile wallet, you have to transfer money through your bank account, debit card or credit card or have to recharge it. Do you know that mobile wallet is both prepaid and post-paid but for pre-paid wallet there is a need to recharge it so that you can use this money for payment? In a postpaid mobile wallet, the account is linked with the wallet itself. So, when you spend money from your wallet, then money will be deducted directly from your bank account at the same time.
In Short, Mobile wallets work by using Near-Field Communications (NFC)-enabled technology or QR code technology. They digitally store payment-related information in an encoded format for security reasons. There may be many variations of how payment information is stored and this varies from wallet to wallet. Apart from this, other information such as store coupons, loyalty programs, and other personal identity-related information is also stored.
- A mobile wallet works by communicating with terminals using various types of information transfer technology
- Most mobile wallets use NFC technology to communicate with payment terminals
Advantages of Mobile Wallet
- Easy accessible: Using mobile wallet for day to day transactions is really simple to begin with. And for this you just have to download the app and create a user ID and password. It is as simple as logging in to your Gmail or Face book account from your smartphone.
- It is simple to add or load money: You can add money to your wallet easily by net banking, credit card or debit card. With this, you can save time in visiting a bank, queue etc.
- Purse or any other type of wallet can be stolen or can be lost anywhere but the mobile wallet is neither stolen nor lost.
- In mobile wallet, money is stored according to your requirement and you don’t have to share your debit or credit card details frequently. So, your money is safe.
- Sometimes payments done via cash are a problem. Like if you have to pay a bill of Rs 480.50 which is not in a round figure then you may face difficulty but with a mobile wallet, payment can be done easily.
- It is not necessary to carry cash every time and mostly mobile wallet provides services. You can shop anytime, anywhere from a mobile wallet.
- Ensures timely payment: You can also make use of the auto facility to make future bill payments automatically from your wallet balance on a pre-determined date.
- Incentives and Promotions: We know that mostly the wallet comes with its own set of incentives. E-wallets give plenty of money-saving offers through the discount, cashback, offers and free gifts. Also, you can make optimum use of promo codes.
Disadvantage of Mobile Wallet
- The mobile wallet technology is easy to use for those who are techno-friendly and require a high-speed Internet connection. So, we can say that mobile network connectivity is the biggest impediment.
- Very few merchants and shopkeepers are listed with the mobile wallet service provider.
- Mobile Wallet has a limit for depositing the money and money that to be spent on the daily basis.
- It does not cater to the needs of the entire population. Most of them are using simple cell phones. Plastic money and m-commerce have not yet caught up completely throughout the entire nation.
So now you must have understood that mobile wallet is a type of digital purse. It can be used for money transactions etc. Or we can say that it is a virtual wallet present in a smartphone in which the money is stored in a digital form. In fact, many wallet companies are offering attractive cash bank schemes etc. to their consumers. If you go for shopping and if it is connected to a mobile wallet service provider then the amount can be paid from the smartphone and also by other ways such as social media, app, website etc.
Different e-Wallet / Mobile Wallet Companies in India
|
E-Wallet/ M-Wallet |
Industry |
Company |
Bank Transfer Allowed? |
Mobile Platform |
Overall Rating (based just on online platform) |
| PayTM | Private | One97 Communications | Yes | Android iOS, Windows Phone, Ovi, Blackberry | 4.4 |
| MobiKwik | Private | One MobiKwik Systems Private Limited | Yes | Android, iOS, Windows Phone | 4.2 |
| Oxigen Wallet | Private | Oxigen Services India Pvt. Ltd. | Yes | Android, iOS, Windows Phone | 3.7 |
| Citrus Wallet | Private | Citrus Pay | Yes | Android, iOS | 3.9 |
| ItzCash | Private | Itz Cash Card Ltd. | Yes | Android, iOS | 4.4 |
| Freecharge | Private | Snapdeal | No | Android, iOS, Windows Phone | 4.3 |
| Axis Bank Lime | Banking Industry | Axis Bank | No | Android, iOS, Windows Phone | 3.6 |
| Airtel Money | Telecom Industry | Airtel | Yes | Android, iOS | 4.2 |
| ICICI Pockets | Banking Industry | ICICI Bank | Yes | Android, iOS | 4.1 |
| Jio Money | Telecom Industry | Reliance | No | Android, iOS, Windows Phone | 4.2 |
| mRupee | Telecom Industry | Tata Teleservices Limited | Yes | Android, iOS, Windows Phone | 3.7 |
| SBI Buddy | Banking Industry | State Bank of India | Yes | Android, iOS | 3.9 |
| Vodafone M-Pesa | Telecom Industry | Vodafone | Yes | Android, iOS, Windows Phone | 4.2 |
| HDFC PayZapp | Banking Industry | HDFC Bank | Yes | Android, iOS | 4.0 |
So now you may have come to know about the mobile wallet and how does it work with advantages and disadvantages.
5)IMPS – Immediate Payment Service
Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) is an initiative of National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). Immediate Payment Service is an instant money transfer service through electronic media. To avail the facility, both the sender and receiver of money needs to be registered for mobile banking service of their respective banks.
IMPS offers an instant, interbank electronic fund transfer service through mobile phones. IMPS is an emphatic tool to transfer money instantly within banks across India through mobile, internet and ATM which is not only safe but also economical both in financial and non-financial perspectives Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) public launch happened on 22nd November 2010 by Smt. Shyamala Gopinath, DG RBI at Mumbai and this service is now available to the Indian public.
This service is available 24/7, throughout the year including on Sundays and any Bank Holidays. You will need IFSC code + account number of the recipient to transfer funds using IMPS facility. It works on real time.
However, at times, due to heavy traffic or some technical issue, you may not receive the fund on instant basis. But then, no need to panic because as soon as you transfer the fund you get the valuation date of transfer which you can check on your net banking by checking the status of your fund under IMPS category.
When to use: When you need to transfer money on an instant basis where time becomes a major constraint, then use IMPS. Moreover, if your transaction amount is between Rs.10000 and Rs 2 lakh, then IMPS is preferable because the service provided to you is on an instant basis with the same service tax as applicable for NEFT.
List of Banks Offering IMPS Money Transfer in India
Some of the top banks offering the IMPS facility are listed as follows:
- AU Small Finance Bank
- Equitas Small Finance Bank
- Jana Small Finance Bank
- Fincare Small Finance Bank
- Ujjivan Small Finance Bank
- ESAF Small Finance Bank
- DBS Bank
- SBI
- HDFC Bank
- ICICI Bank
- Axis Bank
- Citibank
- Kotak Bank
- Yes Bank
- Bank of Baroda
- India Post Office
- Standard Chartered Bank
- PNB
- South Indian Bank
- IDBI Bank
- Andhra Bank
- Indian Bank
- Canara Bank
- UCO Bank
Channels for Transacting
- Mobile Banking (MB)
- Retail Internet Banking (RIB)
- Corporate Internet Banking (CIB)
How to Transfer Funds through IMPS?
Transferring funds using IMPS is easy and quick, and involves the least effort. This can be done using the mobile banking facility of the concerned bank. To know how to transfer funds through IMPS, follow the below-mentioned steps:
Objectives of IMPS
- To enable bank customers to use mobile instruments as a channel for accessing their banks accounts and remit funds
- Making payment simpler just with the mobile number of the beneficiary
- To sub-serve the goal of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in electronification of retail payments
- To facilitate mobile payment systems already introduced in India with the Reserve Bank of India Mobile Payment Guidelines 2008 to be inter-operable across banks and mobile operators in a safe and secured manner
- To build the foundation for a full range of mobile based Banking services.
The key features of IMPS Funds Transfer are as follows:
The IMPS payment facility offers a number of features that are highly beneficial in the digital world. These are listed as follows:
The participants for IMPS are as follows:
- Remitter (Sender)
- Beneficiary (Receiver)
- Banks
- National Financial Switch – NPCI
Pre-Requisites for IMPS Registration for Remitter:
- Register yourself with the mobile banking service of the bank.
- Get Mobile Money Identifier (MMID) and MPIN from the bank
- Download Software (Application) for mobile banking (ensure the compatibility of mobile with the application) or use the SMS facility in your mobile if your bank provides IMPS on SMS
Registration for Beneficiary:
- Link your mobile number to the account in the respective bank.
- Get Mobile Money Identifier (MMID) from the bank
Funds Transfer / Remittance
- Using Mobile number & MMID (P2P)
- Using Account number & IFS Code (P2A)
- Using Aadhaar number (ABRS)
Using Mobile number & MMID (P2P)
IMPS offer an instant, 24*7 interbank electronic fund transfer service capable of processing person to person, person to account and person to merchant remittances via mobile, internet and ATM’s. It is a multichannel and multidimensional platform that make the payments possible within fraction of seconds with all the standards and integrity maintained for security required for even high worth transactions.
Sender & Receiver
– Have to register for Mobile Banking & get a unique ID called “MMID”
- Generation of MMID is a One-time process.
- Remitter (Sender) transfer funds to beneficiary (Receiver) using Mobile no. & 7digit MMID of beneficiary.
Additional information’s:
MMID – Mobile Money Identifier (7 digit code)
Each MMID is linked to a unique Mobile Number. Different MMIDs can be linked to same Mobile Number
Using Account number & IFS Code (P2A)
Presently, IMPS Person-to-Person (P2P) funds transfer requires the Remitter customer to make funds transfer using Beneficiary Mobile Number and MMID. Both Remitter as well as Beneficiary needs to register their mobile number with their respective bank account and get MMID, in order to send or receive funds using IMPS.
There may be cases where Remitter is enabled on Mobile Banking, but Beneficiary mobile number is not registered with any bank account. In such cases, Remitter shall not be able to send money to the Beneficiary using Mobile Number & MMID.
Hence on the merit of the feedback received from the banking community as well as to cater the above mentioned need, the IMPS funds transfer has been made possible using Beneficiary account number and IFS code as well, in addition to Beneficiary mobile number and MMID.
Additional information’s:
IFS Code – 11 digit alphanumeric number, available in the users Cheque book.
Using Aadhaar number (ABRS)
In ABRS, a remitter can initiate IMPS transaction using the beneficiary’s AADHAAR number, which acts as a financial address & which will be linked to the beneficiaries account number. ABRS facilitates in simplifying the IMPS payment initiation process as in this service the customer will have to input only AADHAAR number of the beneficiary for initiating an IMPS transaction. Another important utility of this service will be in disbursal of subsidy payment i.e. Electronic Benefit Transfer (EBT)/ Direct Benefit transfer (DBT) by the Government. ABRS will act as a catalyst in expanding financial Inclusion reach.
Query Service on Aadhaar Mapper (QSAM)
To facilitate the effective implementation of ABRS, a new feature is being added to the existing NUUP (USSD based platform on *99#) service. Under this new service, known as “Query Service on Aadhaar Mapper” the customer will be able to know : –
- Whether his/her AADHAAR number is seeded/linked to any bank account number or not?
- If yes, then with which bank and when was it last updated?
KEY POINTS to Remember
For transactions initiated using Mobile, transactions will be authenticated using mobile number & MPIN.
Currently, our Bank is offering Funds Transfer under the following products –
- Person–to–Person (P2P)
- Person–to-Account (P2A).
Delivery Channels for IMPS Funds Transfer.
Following delivery channels has been enabled for IMPS funds Transfer –
- SMS Channel .
- Internet Banking.
- Mobile Banking.
Funds transfer limit – Existing Limits will remain applicable as under –
Fees and Charges of IMPS
IMPS fund transfer allows the bank to charge certain fees and charges. The charges, however are based on the amount of funds transferred, as shown in the table below:
| Amount | Charges |
|---|---|
| Less than or equal to ₹ 10,000 | ₹ 2.5 |
| More than ₹ 10,000 up to ₹ 1 lakh | ₹ 5 |
| More than ₹ 1 Lakh to up to ₹ 20 Lakh | ₹ 15 |
Note
6)NEFT -National Electronic Funds Transfer
NEFT stands for National Electronic Funds Transfer. It is regarded as a convenient method of sending money to other bank accounts. Various individuals, firms and corporates have benefitted by using this particular fund transfer system under internet banking without the need for physically visiting the bank.
This is a nation-wide payment system maintained by RBI which facilitates one to one fund transfer. NEFT operates on a Deferred Net Settlement basis under which funds are transferred in half-hourly batches. In order to transfer money using NEFT, both the bank branches should be NEFT-enabled. To check whether your bank branch is NEFT-enabled, you can call the customer service of your bank.
How to send money using NEFT?
You should follow the procedure given below to send money using NEFT. You must have registered for your bank’s internet banking facility to be able to do so.
- Login to your internet banking portal using your Customer ID and Password.
- Go to the Fund Transfer section and select NEFT.
- You will be required to add beneficiary first. Enter the name, account number, IFS Code and branch name of the beneficiary’s bank account.
- Once the beneficiary is successfully added, you can transfer fund by entering the amount you want to send.
- Select the account from which you wish to send the amount.
- Click on ‘confirm’.
What is NEFT Transfer Operation Procedure?
Let us find out what is NEFT transfer process:
- The NEFT process starts when a remitter sends funds to the beneficiary’s account.
- When a NEFT request is generated, the originating bank branch creates a message and sends it to its pooling centre, called as NEFT Service Centre.
- From the pooling centre, the message is forwarded to the NEFT Clearing Centre which is operated by National Clearing Cell, Reserve Bank of India.
- At the Clearing Centre, the sorting is done for money transfer transactions destination bank-wise and accounting entries are done to receive funds from the remitter’s bank (debit) and provide the funds to the destination bank (credit). Later, remittance messages (bank-wise) are offered to the destination banks through their respective pooling centre (NEFT Service Centre).
- The destination banks are served with inward remittance messages from the Clearing Centre and carry forward the credit to the beneficiary customers’ accounts.
NEFT scheme is extremely successful for online transactions since it saves a lot of time for the customer. Everything is processed over the internet under a designated time frame which has been formulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
7)Real-time gross settlement (RTGS)
Over the years, innovative technology has revolutionized Indian payment systems. Customers today have a wide choice of avenues to quickly transfer their funds to customers of other banks at low charges, known as inter-bank funds transfer. The table below summarizes the key features of three main quick payment systems in India.
Key Features & Difference Between NEFT, RTGS & IMPS
| Payment System | Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| RTGS full form: Real-Time Gross Settlement |
|
|
| NEFT full form: National Electronic Funds Transfer. |
|
|
| IMPS full form: Immediate Payment Service. |
|
|
8)Recurring Payment/ Standing Instruction(SI)
Recurring billing lets merchants charge customers on regular intervals through saved billing schedules. Accept these payments via credit card, debit card or electronic check.
Applicable categories- Travels for Subscriptions, Bill Payments/Utilities, Insurance, IT & Software Services for subscription, Entertainment for subscription, NGO
9) Equated monthly instalment (EMI)
EMI or equated monthly instalment, as the name suggests, is one part of the equally divided monthly outgoes to clear off an outstanding loan within a stipulated time frame.
Description: The EMI is dependent on multiple factors, such as:
- Principal borrowed
- Rate of interest
- Tenure of the loan
- Monthly/annual resting period
For a fixed interest rate loan, the EMI remains fixed for the entire tenure of the loan, provided there is no default or part-payment in between. The EMI is used to pay off both the principal and interest components of an outstanding loan. The first EMI has the highest interest component and the lowest principal component. With every subsequent EMI, the interest component keeps on reducing while the principal component keeps rising. Thus, the last EMI has the highest principal component and the lower interest component.
In case the borrower makes a pre-payment through the tenure of a running loan, either the subsequent EMIs get reduced or the original tenure of the loan gets reduced or a mix of both. The reverse happens when the borrower skips an EMI through the tenure of the loan (EMI holiday or cheque dis-honor/bounce or insufficient balance in case of auto deduction of EMI or a default); in that case either the subsequent EMIs rise or the tenure of the loan increases or a mix of both, apart from inviting a financial penalty, if any.
Similarly, in case the rate of interest reduces through the tenure of the loan (as in the case of floating rate loans) the subsequent EMIs get reduced or the tenure of the loan falls or a mix of both. The reverse happens when the rate of interest rises.
10) UPI – Unified Payments Interface
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is a payment system that allows users to link more than one bank account in a single smartphone app and make fund transfers without having to provide IFSC code or account number.
- This is a real-time payment system where funds are credited instantly on a real-time basis.
- Apart from sending money, users will also be able to make ‘collect’ requests. A user will only have to use a virtual address, known as a Virtual Payment Address (VPA) to carry out any transaction.
- UPI makes the fund transfer process easier, faster and hassle-free. There is no need to go through the cumbersome process of entering all bank details. Users can both send and receive money using a VPA.
Features of UPI
The UPI interface allows users to avail a number of services. The following are the transactions that can be carried out using UPI:
- Sending and receiving funds
- Making requests for funds
- Pay merchants through QR code scanning via BHIM
- Pay for cabs
UPI Transaction Limit :UPI has a certain per day and per transaction limit on the value of transactions. Given below are the updated transaction limits that is followed by some of the top banks in the country:
- (Per transaction limit and transaction limit per day Rs.1 lakh )
- In most cases, the maximum number of UPI transactions that can be made per day is around 20
- While some banks like ICICI, HDFC, SBI and PNB allow you to send Rs.1 lakh per transaction, other banks may allow you to send only Rs.10,000 per transaction.
- The maximum limit for BHIM UPI is Rs.10,000 per transaction and Rs.20,000 in a 24 hour window.
- The transaction limit may be revised from time to time.
What are the transactions that can be performed using UPI?
The following are the type of the transactions, that can be conducted through UPI:
- Remittances: If you need to send or transfer money quickly to your friends or family, or somebody needs money urgently, this app this correct click or tap for the individual.
- Bill payments: From Utility bills to your communication bill payments can be made.
- Merchant transactions: This could be anything from booking movie tickets online to buying groceries on an online app.
How to Make Payments Using UPI?
This is how UPI works when sending money to another party:
- You need to first Log on to your bank’s UPI application
- Once logged in choose the option for sending money or payment.
- You need to then enter the beneficiary’s virtual id and the amount you wish to send followed by the account number.
- Once you get a confirmation message, do check the payment details to confirm the payment.
- You need to then key-in the MPIN.
- You will get a notification that will know whether the payment ‘successful’ or ‘failure’ message
The conventional UPI collect flow, allows bank account holders to transact using a Virtual Payment Address (VPA), without entering additional bank information.
UPI QR Code Based Payments
You can make direct bank payments to anyone on UPI using their UPI ID or scanning their QR with the BHIM app. You can also request money through the app from a UPIID. Send money by entering UPI ID , account number, aadhaar or by scanning a QR. Request money from other UPI users by entering their UPI ID.
Benefits of UPI Intent:
While you enjoy the benefits such as higher conversion rates, decrease in abandoned carts and a decrease in time to complete the payment, your customers are also benefited in the following ways:
- No need to handle push or SMS notifications
- No need to switch between applications to complete a payment (merchant, SMS, app)
- No need to remember their VPAs
Understanding the Intent flow#
- In the UPI Intent flow, the customer selects UPI as the payment method in your website or app. A list of UPI apps supporting the intent flow is displayed.
- Customers select their preferred app. The UPI app opens with a pre-populated payment details displayed.
- Customers enter the UPI PIN to complete their transactions.
- After the successful payment, the customer is redirected to your app or website.
To know more about the UPI Intent on Android apps, refer the Android UPI Intent flow.
UPI Intent FLOW:
- Customer selects UPI as the payment mode in merchant app/website
- Customer is shown the list of UPI apps installed on their phone that support intent flow
- Customer selects their preferred UPI application
- UPI App opens with pre-populated payment details
- Customer enters the UPI PIN / MPIN to complete the transaction
- Customer gets confirmation of the payment being successful on the app/website
BENEFITS OF USING UPI INTENT:
- Customers need not remember and enter VPA
- Customers don’t have to handle push/SMS notifications anymore
- Customers no longer have to juggle 3 apps (merchant, SMS, UPI app) while doing a transaction
- Improved payment process leads to higher conversion rate, decrease in abandoned carts, and shorter time to complete the payment
- Ease of making payments results in an optimal user experience for customers
Most of the UPI apps have added support for intent flow, including BHIM, PhonePe, Tez, Whatsapp etc. and various UPI enabled bank apps.
11) Payment Link
In simple terms, a payment link is an online payment method where a request for online payment which is generated and shared by the merchant to the customer, to make instant online payments. Accepting payments via link sharing is the easiest and fastest way for both customers and merchants. The payment collection is done either via the payment link or a QR code.
How do payment links work?

Generate a payment link, share the link and collect payment instantly, it’s as simple as that.
To elaborate further,
- Merchant generates a payment link
- Merchant shares the payment link
- Customer gets the link
- Customer clicks on the link
- The link then redirects the customer to the secure payment page
- Customers make an online payment with offered methods(wallet, UPI, cards, net banking, etc)
- Merchant gets notification after successful payment.
Benefits of payment links for merchants:
- Security: Creating and sharing a payment link is backed with a secured payment gateway. Most payment link solutions come with fraud and charge back handling and assist merchants and customers with hassle-free transactions.
- Reduce over head cost: Accepting payments via link eliminates the need for any external physical payment acceptance devices (like POS terminals) or any third-party application. This saves time and cost for installation, maintenance, and training.
- Customised messages: Payment links can be shared on any social media or messaging platforms, Merchants can attach a customized message while creating a payment link to attract customers, to promote other products, etc.
- Bulk orders/ split payments/ EMI Payments: Accepting payments via payment links allows merchants to create payment links for flexible, variable payment orders, or accepting payments in installments.
- Better customer experience: Accepting payments via link sharing caters to the need of an Omnichannel business, as it is always available on the merchant’s mobile phone. Payment links offer on the spot payments with faster transaction rates. This improves the overall customer experience contributing to an increase in revenue.
- Happy Customers : Payment acceptance via link sharing improves the service level and increases convenience for merchants as well as customers. With flexible payment links, customers can pay from wherever they want with the preferred payment option. It increases customer satisfaction and can be used to build a loyal customer base.
Give your customers the flexibility to pay and they will surely love to shop with you.
12)Aadhaar Enabled Payment System(AEPS)
It connects the banks with the un-banked and the under-banked
- It is a type of payment system that is based on the Unique Identification Number and allows Aadhaar card holders to seamlessly make financial transactions through Aadhaar-based authentication. In simple term AEPS is nothing but an Aadhaar-enabled payment system through which you can transfer funds, make payments, deposit cash, make withdrawals, make enquiry about bank balance, etc.
- The AEPS system aims to empower all sections of the society by making financial and banking services available to all through Aadhaar.
- The AEPS system leverages Aadhaar online authentication and enables Aadhaar Enabled Bank Accounts (AEBA) to be operated in anytime-anywhere banking mode through Micro ATMs.
- This system is controlled by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- The 5 Aadhaar enabled basic types of banking transactions are: Cash Withdrawal, Cash Deposit, Aadhaar to Aadhaar Funds Transfer, Gateway Authentication Service.
Objectives
- To empower a bank customer to use Aadhaar as his/her identity to access his/ her respective Aadhaar enabled bank account and perform basic banking transactions like cash deposit, cash withdrawal, Intrabank or interbank fund transfer, balance enquiry and obtain a mini statement through a Business Correspondent
- To sub-serve the goal of Government of India (GoI) and Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in furthering Financial Inclusion.
- To sub-serve the goal of RBI in electronification of retail payments.
- To enable banks to route the Aadhaar initiated interbank transactions through a central switching and clearing agency.
- To facilitate disbursements of Government entitlements like NREGA, Social Security pension, Handicapped Old Age Pension etc. of any Central or State Government bodies, using Aadhaar and authentication thereof as supported by UIDAI.
- To facilitate interoperability across banks in a safe and secured manner.
- To build the foundation for a full range of Aadhaar enabled Banking services.
How to use AEPS?
- Go to a micro ATM or banking correspondent(BC)
- Provide Aadhaar number and bank name
- Choose the type of transaction you want to make
- Provide verification through fingerprint/iris scan
- Collect your receipt
Features & Benefits of AEPS
- Easy to use
- Safe and secure payment method
- Interoperable across various banks
- Encourages financial inclusion and serves the under banked sections of society
- Through AEPS, all bank account holders will be able to access their bank accounts through Aadhaar authentication
- With AEPS, the only information required to initiate a transaction is Aadhaar number and bio metric information
- AEPS facilitates disbursements of Government schemes like NREGA, Social Security pension, Handicapped Old Age Pension etc. of any Central or State Government bodies using Aadhaar authentication.
How Does AEPS Work?
The AEPS machine works like a Point of Sale (POS) machine. Instead of a debit/credit card pin, the merchant will have to key in the customer’s Aadhaar number and authenticate the transaction using the customer’s bio metric data.
You will require the following formation to carry out an AEPS transaction:
- Bank’s Issuer Identification Number (IIN) or name
- Aadhaar Number
- Fingerprint
12) WhatsApp Pay
On 5th Nov. 20, WhatsApp rolled out its innovative, chat based, payments services,‘WhatsApp Pay’ in India on UPI platform of NPCI that enables transactions with over 160 supported banks/mobile wallet operators. With this, it is slated to give a tough competition to existing players like Paytm, Google Pay, Walmart-owned PhonePe and Amazon Pay.
However, even with a 400-million user base in the country, WhatsApp Pay will only be rolled out to 20 million WhatsApp users. That’s because NPCI has said that a 30% cap will be implemented on total payment volumes via every third party payments app from January 1, 2021.
Currently, it is working with five banks in India – ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, Axis Bank, the State Bank of India, and Jio Payments Bank – and people can send money on WhatsApp to anyone using a UPI supported app.
To send money on WhatsApp in the country, it’s important to have a bank account and debit card in India. The Facebook-owned messaging app will send instructions to banks, also known as payment service providers, that will initiate the transfer of money via UPI between sender and receiver bank accounts.
With this, WhatsApp users can send money to anyone using a UPI supported app.While using WhatsApp for payments, one needs to enter a personal UPI PIN for each transaction.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to enable, send or receive money via WhatsApp Pay:
- Click on the WhatsApp app on your mobile phone and select the three-dotted icon visible on the top right corner of your screen.
- Select ‘Payments‘, then ‘Add payment method’
- A list of bank names will be on your screen.
- After you finish selecting your bank name, your cell number, which is linked with the bank, will be verified.
- For verification, a user needs to select ‘Verify’ via SMS.
Note: You need to make sure the WhatsApp number is the same as the one linked to your bank a/c.
- Once you’re done with the verification process, a user then needs to complete setting up payments.
- A UPI Pin is mandatory for carrying out transactions on WhatsApp similar to how it’s on other apps.
Following this, you can see the chosen bank on the payments page.
If user wants to send or receive money :
- Open any chat on WhatsApp and select the ‘attachment’ icon.
- Click on ‘Payment’ and add the money you want to send to the person. A user can also add a note.
- To finish the payment process on WhatsApp, you will have to enter your UPI PIN.
- After you finish you transaction, you will get a confirmation message.
Payments on WhatsApp is now available for users on the latest version of the iPhone and Android app.
Here are key things to know about the WhatsApp payment service:
- Payments (service) on WhatsApp is available for people on the latest version of the iPhone and Android app. However, it is being rolled out in a phased manner, starting with a maximum registered user base of 20 million in UPI. So, some users may not be available to use WhatsApp immediately.
- WhatsApp Pay is free and users won’t be charged a transaction fee. However, the limit for a transaction on WhatsApp’s payment service is Rs 1 lakh.
- To use WhatsApp payment, one must have an Indian number and Indian bank account. People using international numbers will not be able to use WhatsApp’s payment service.
- The payment service will be currently available in 10 Indian language versions of WhatsApp.
- These payments, as said by WhatsApp, is designed with a strong set of security and privacy principles, including entering a personal UPI PIN for each payment.
So, it is completely secured.
Registering less than 1% of the total UPI transactions in the month of November 2020, it is indeed a slow start for WhatsApp Pay. As per a report shared by the ET Telecom, WhatsApp Pay saw over 20 million transactions last month.To get a perspective of how small this number is, the overall market saw a total of 2.2 billion UPI transactions in November 2020. Compared to October’s 2.1 billion total transactions, it is a growth of 7% for total UPI transactions in the country.
A thing worth noting here is that WhatsApp Pay currently allows only peer-to-peer (P2P ) payments. The peer-to-merchant (P2M) payments haven’t been allowed until now. WhatsApp has over 400 million monthly active users in the country, so there is no denying that this number will increase as time passes by.
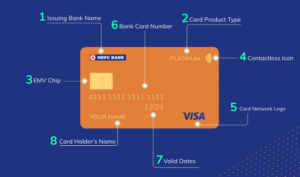



0 Comments